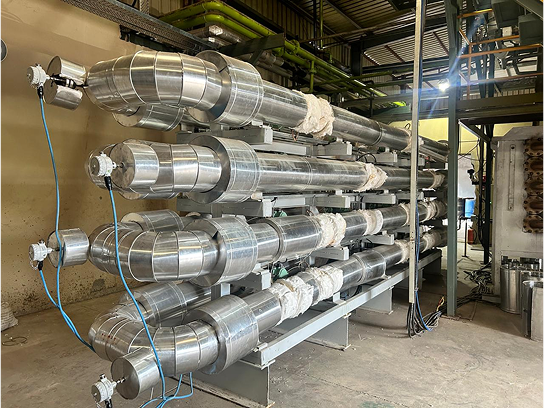
Plug Flow Reactor Characteristic
Boost efficiency with high-performance Plug Flow Reactors. Get superior control, faster reactions, and reliable results from top manufacturers in India.
TOPSE’s offerings :
- The characteristics of a plug flow reactor include the following
- The reactants in a plug-flow reactor flow throughout the reactor in a continuous flow with little to no mixing.
- The reaction in PFR occurs when the reactants move with the reactor length
- The concentration of reactants changes with the reactor’s length and the rate of reaction is generally higher at the entry.
- These reactors are frequently used for reactions wherever a high amount of change is necessary and wherever the reaction speed is not responsive to absorption changes.
- The residence time within the PFR is normally short.
- The biofilm forms close to the air-liquid interface simulating environments such as the oral cavity, wet rock surfaces, and shower curtains.
- This type of reactor generates a consistent biofilm in low shear that can be utilized like the static glass coupon reactor to check microbicide effectiveness.
- The biofilm of this reactor is analyzed easily with different methods like viable plate counts, determination of thickness & light microscopy.
The plug flow reactor advantages include the following. :
- The PFR advantage over CSTR is that this reactor has a low volume for a similar space-time & conversion level.
- The reactor needs less space & that the quantity of conversion is high within PFR as compared to CSTR for a similar reactor volume.
- This reactor is used frequently to decide the gas-phase catalytic kinetics process.
- These reactors are very effective in handling reactions & for a large group of “typical” reactions effect within higher conversion rates for each reactor volume as compared to CSTR (Continuous Stirred-Tank Reactors)
- The reaction in PFR occurs when the reactants move with the reactor length.
- These reactors are frequently used for reactions wherever a high amount of change is necessary and wherever the reaction speed is not responsive to absorption changes.
The plug flow reactor disadvantages include the following :
- In a PFR, exothermic response performance is hard to control due to the broad range of temperature profiles.
- For a PFR, maintenance & operational expenditures are costly as compared to the CST.
- Temperature control is difficult for a reactor.
- Hot spots occur in the reactor whenever used for exothermic reactions.
- It is hard to control because of composition & temperature variations.